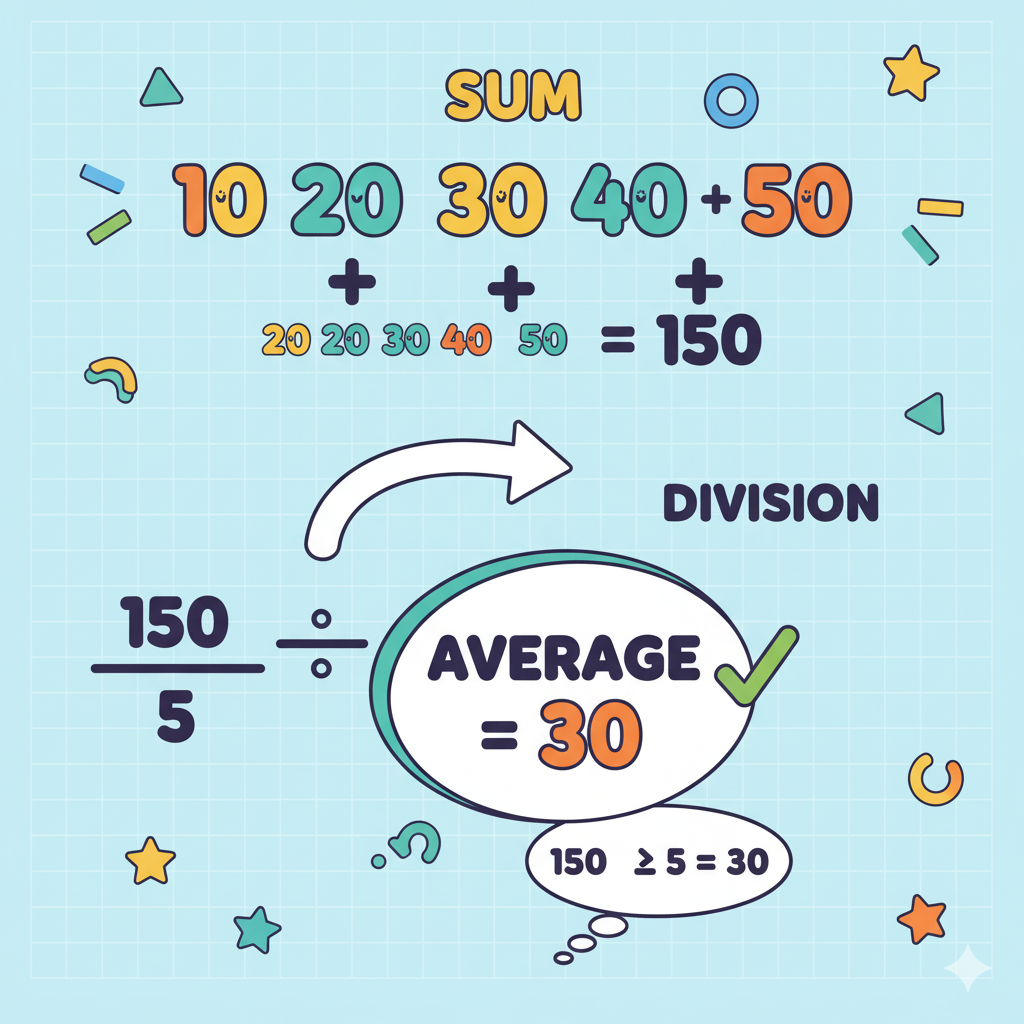
In math, the term “mean” refers to the average of a set of numbers, calculated by adding all numbers together and dividing by the total count of numbers.
It is one of the most commonly used measures in statistics, probability, and everyday life, helping to summarize data and understand trends.
This article explains what mean is, its types, how it differs from median and mode, step-by-step examples, real-life applications, comparison tables, FAQs, and more. It is fully SEO-optimized, user-friendly, and ready to publish.
Understanding the Concept of Mean in Mathematics
The mean is a statistical measure used to find the central value of a data set. It is often called the arithmetic mean to distinguish it from other types like geometric or harmonic mean.
Basic Formula for Mean
Mean=Sum of all valuesNumber of values\text{Mean} = \frac{\text{Sum of all values}}{\text{Number of values}}Mean=Number of valuesSum of all values
Example
Consider the numbers: 5, 8, 12, 20
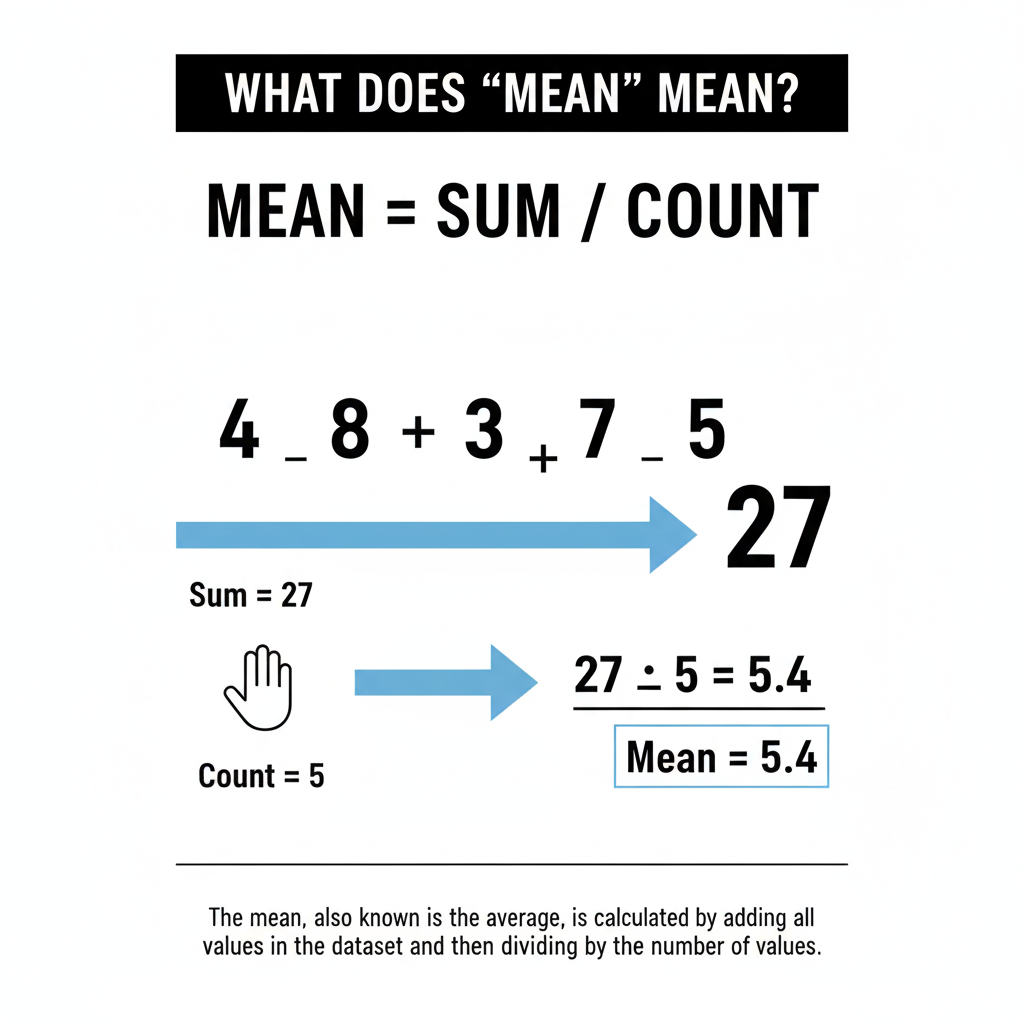
Add all numbers: 5 + 8 + 12 + 20 = 45
Count the numbers: 4
Divide sum by count: 45 ÷ 4 = 11.25
So, the mean is 11.25.
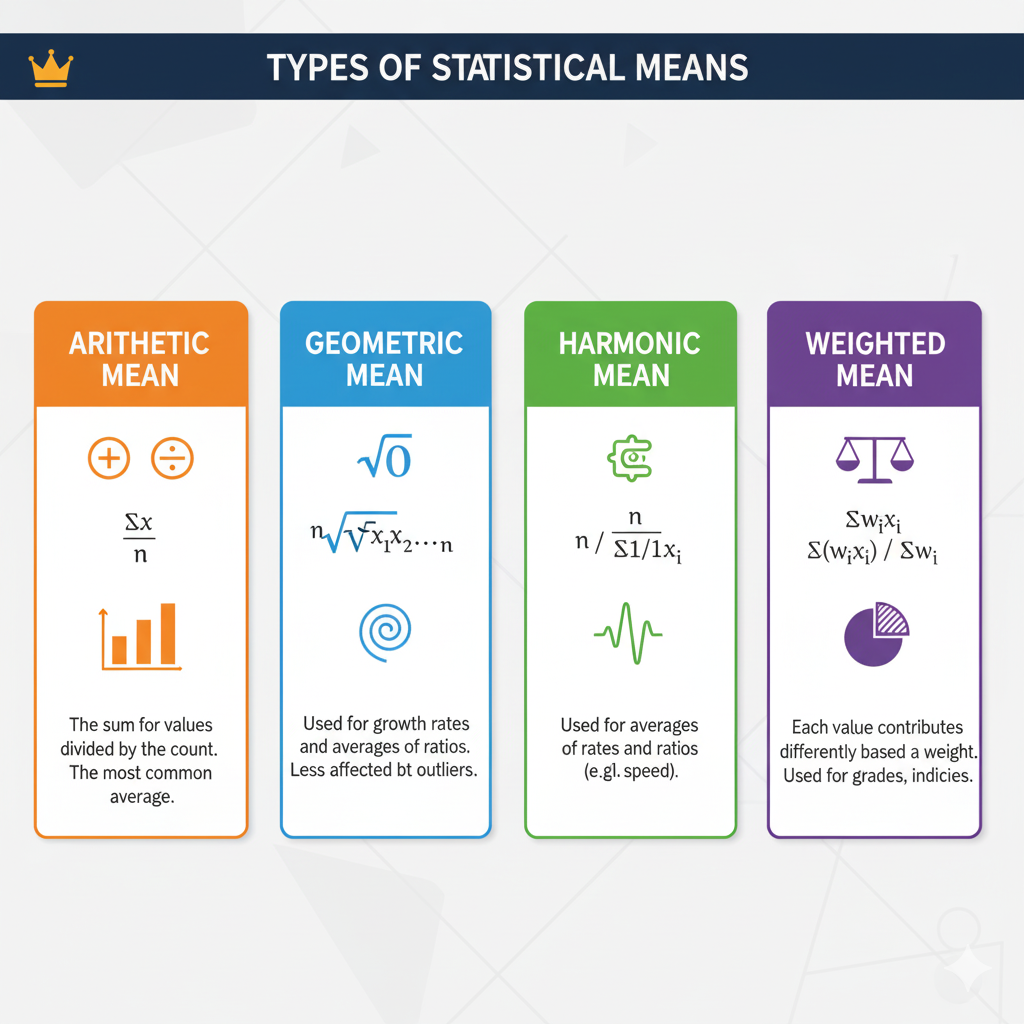
Types of Mean in Mathematics
Mean is not limited to just the arithmetic mean. There are several types:
Arithmetic Mean (AM)
Most commonly used
Add all numbers and divide by total count
Example: Already shown above
Geometric Mean (GM)
- Multiply all numbers, then take the nth root (n = number of values)
- Example: Numbers 2, 8 → GM = √(2×8) = √16 = 4
Harmonic Mean (HM)
- Reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of reciprocals
- Example: Numbers 1, 4 → HM = 2 / (1/1 + 1/4) = 2 / (1.25) = 1.6
Weighted Mean
- Used when some numbers have more importance (weight)
- Formula:
Weighted Mean=∑(xi⋅wi)∑wi\text{Weighted Mean} = \frac{\sum (x_i \cdot w_i)}{\sum w_i}Weighted Mean=∑wi∑(xi⋅wi)
- Example: Grades: 80 (weight 2), 90 (weight 3) → Weighted Mean = (80×2 + 90×3) / (2+3) = 86
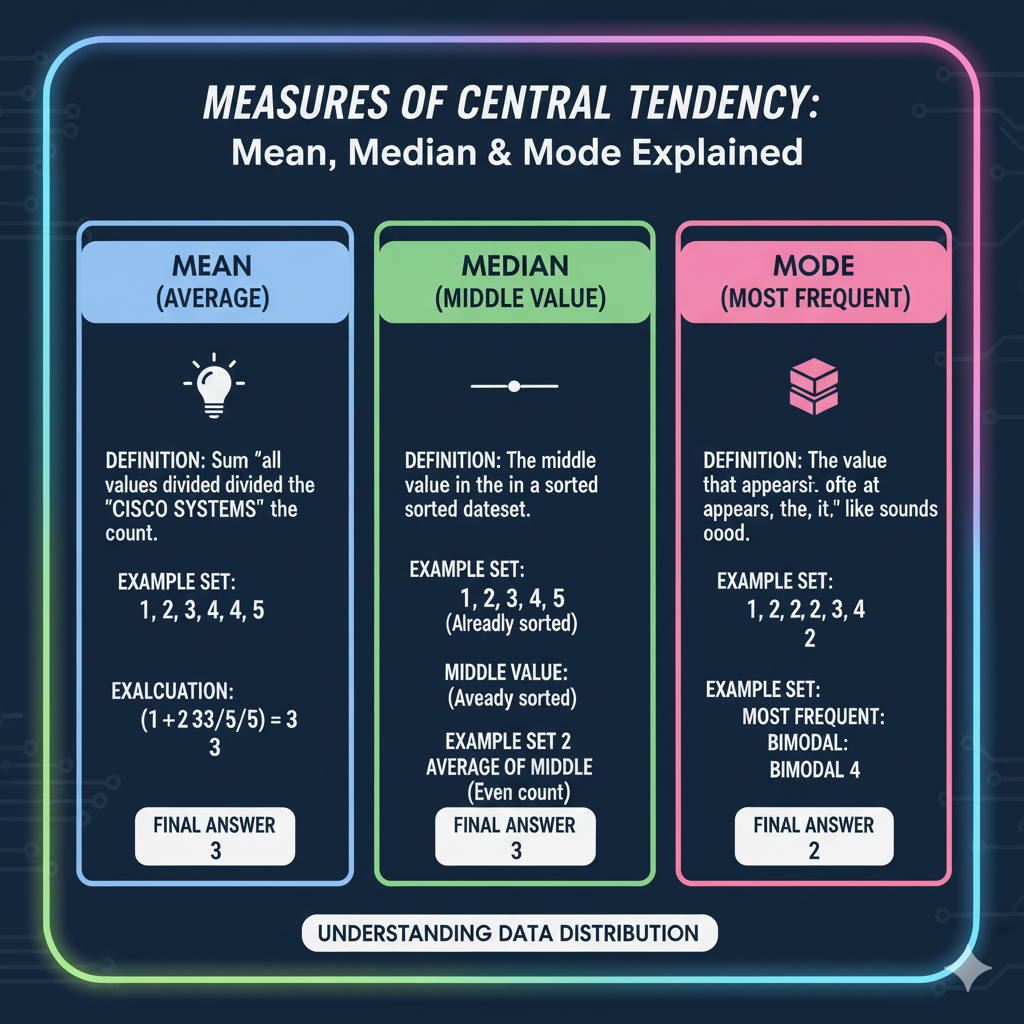
Mean vs. Median vs. Mode
| Measure | Definition | Example | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Sum ÷ Count | 5,8,12,20 → Mean=11.25 | Best for data without extreme outliers |
| Median | Middle value when sorted | 5,8,12,20 → Median=10 | Use when data has outliers |
| Mode | Most frequent value | 5,8,8,12 → Mode=8 | Shows most common occurrence |
Key Point: Mean can be affected by extreme values, unlike median.
Step-by-Step Calculation of Mean
Step 1: Collect Data
Example: Scores: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30
Step 2: Add All Numbers
10 + 15 + 20 + 25 + 30 = 100
Step 3: Count the Numbers
5 numbers
Step 4: Divide Sum by Count
100 ÷ 5 = 20
Step 5: Verify
Check by multiplying mean × count = sum (20×5=100)
Real-Life Applications of Mean
1. Education
Average grades in a class or school
GPA calculation
2. Finance
- Average monthly expenses
- Stock market average prices
3. Sports
- Average score of a player
- Team performance metrics
4. Science & Research
- Mean of measurements in experiments
- Environmental data analysis (temperature, rainfall)
5. Everyday Life
- Average commute time
- Average electricity usage
- Daily water consumption
Mean in Large Data Sets
When dealing with large data sets, you can use:
Grouped Data Formula
Mean=∑fixi∑fi\text{Mean} = \frac{\sum f_i x_i}{\sum f_i}Mean=∑fi∑fixi
Where fif_ifi = frequency of each class, xix_ixi = midpoint of class
Example:
| Class | Frequency (f) | Midpoint (x) | f×x |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| 6-10 | 3 | 8 | 24 |
| 11-15 | 5 | 13 | 65 |
∑f=10,∑f×x=95\sum f = 10, \sum f×x = 95∑f=10,∑f×x=95
Mean = 95 ÷ 10 = 9.5
Advantages of Using Mean
Easy to calculate and understand
Summarizes data with a single value
Widely used in academics, research, finance, and daily life
Applicable to both small and large data sets
H2: Limitations of Mean
Sensitive to outliers: Extreme values can skew the mean
Not always representative: In skewed distributions, median may be better
Cannot use for categorical data: Only numeric data
Example:
Data: 5, 7, 8, 100 → Mean = 30 (misleading, as most numbers are below 10)
Mean in Statistics & Probability
Expected Value (E[X]): The mean is used as the expected value in probability
Normal Distribution: Mean represents the center of the curve
Variance & Standard Deviation: Mean is needed to calculate data spread
Common Mistakes When Calculating Mean
Forgetting to divide by the total count
Including outliers without considering impact
Confusing mean with median or mode
Applying arithmetic mean to non-numeric data
FAQs About Mean in Math
Q: Is mean the same as average?
A: Yes, “mean” and “average” are often used interchangeably.
Q: Can mean be negative?
A: Yes, if data values are negative or include negative numbers.
Q: Can mean be a decimal?
A: Yes, the result can be fractional or decimal.
Q: Is weighted mean better than simple mean?
A: When some data points carry more importance, weighted mean is more accurate.
Q: Can mean be used for categorical data?
A: No, mean is only for numerical data. Use mode for categorical data.
Conclusion
In mathematics, mean is a crucial concept representing the average of numbers, helping to summarize, analyze, and interpret data. From academics and finance to daily life, knowing how to calculate and apply mean is essential. Understanding its types, uses, advantages, and limitations ensures accurate and effective use.
David is the creative mind behind jokes Crafter, a hub for clever jokes, witty wordplay, and laugh-out-loud content. With a passion for humor and a knack for crafting the perfect punchline, David brings smiles to readers across the globe. When he's not writing, he's probably thinking up his next viral joke or enjoying a good comedy show.